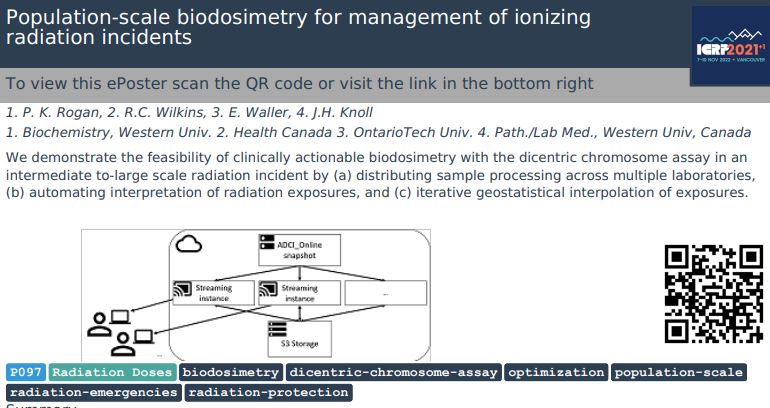
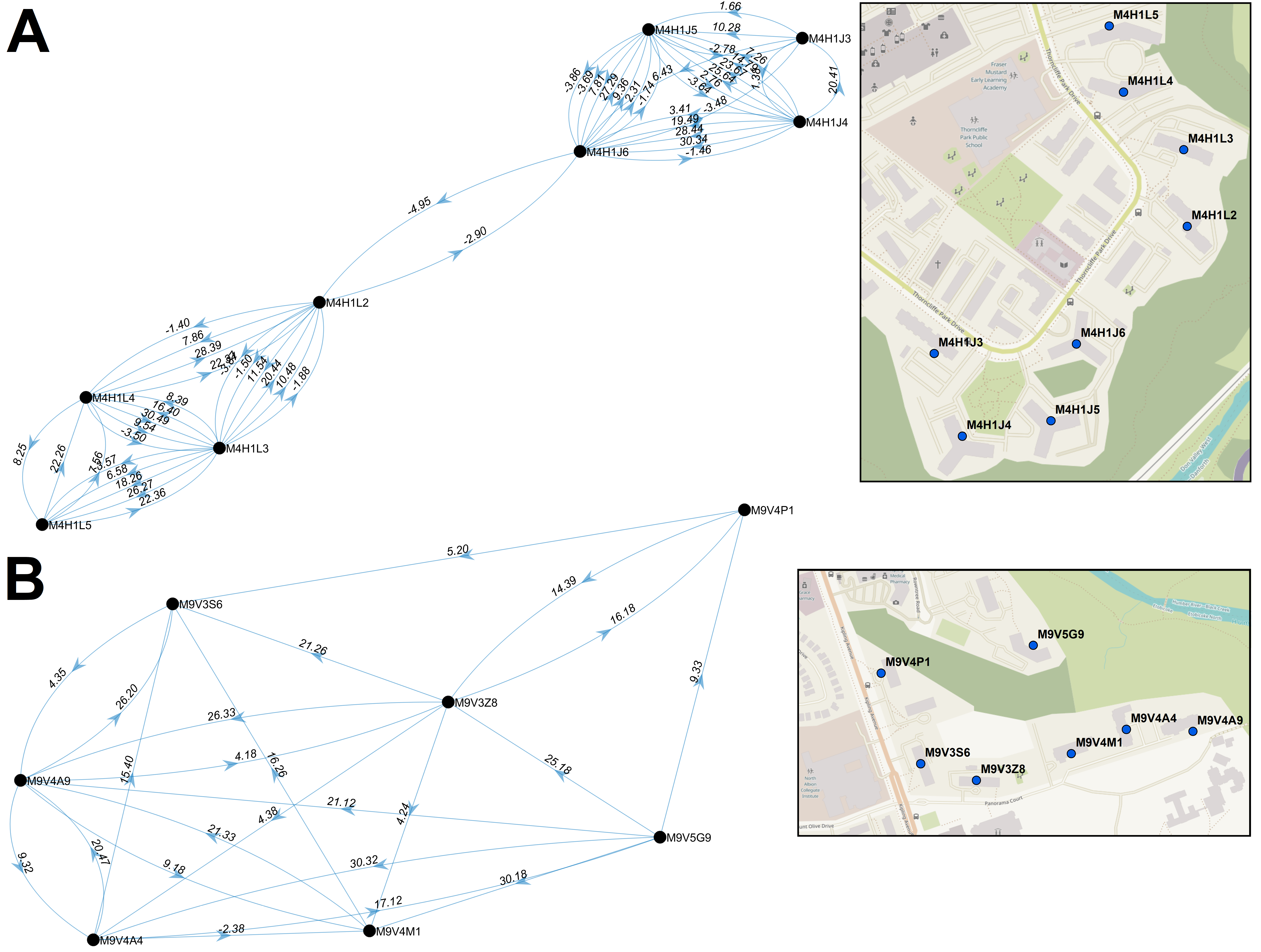
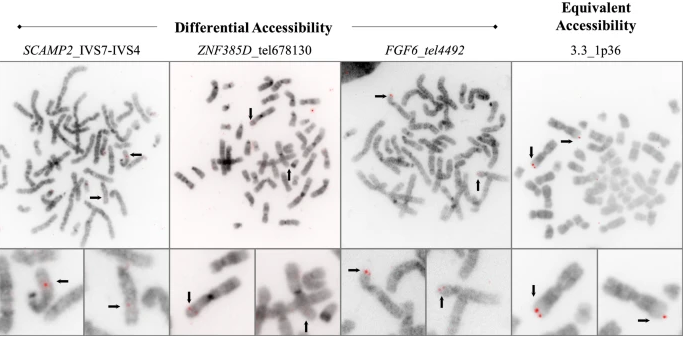
We have contributed our work on transcriptomics to the chapter on Molecular Radiation Biology in:
Radiobiology Textbook (editor Sarah Baatout), published by Springer in October 2023 (open access; link: https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-3-031-18810-7). The citation for the chapter is:
Judith Reindl, Ana Margarida Abrantes, Vidhula Ahire, Omid Azimzadeh, Sarah Baatout, Ans Baeyens, Bjorn Baselet, Vinita Chauhan, Fabiana Da Pieve, Wendy Delbart, Caitlin Pria Dobney, Nina Frederike Jeppesen Edin, Martin Falk, Nicolas Foray, Agnès François, Sandrine Frelon, Udo S Gaipl, Alexandros G Georgakilas, Olivier Guipaud, Michael Hausmann, Anna Jelinek Michaelidesova, Munira Kadhim, Inês Alexandra Marques, Mirta Milic, Dhruti Mistry, Simone Moertl, Alegría Montoro, Elena Obrador, Ana Salomé Pires, Roel Quintens, Nicholas Rajan, Franz Rödel, Peter Rogan, Diana Savu, Giuseppe Schettino, Kevin Tabury, Georgia I Terzoudi, Sotiria Triantopoulou, Kristina Viktorsson, Anne-Sophie Wozny (2023). Molecular Radiation Biology. In Radiobiology Textbook (pp. 83-189). Cham: Springer International Publishing.

 In late 2023, we coauthored a new Open Access textbook on Radiobiology ((https://link.springer.com/
In late 2023, we coauthored a new Open Access textbook on Radiobiology ((https://link.springer.com/